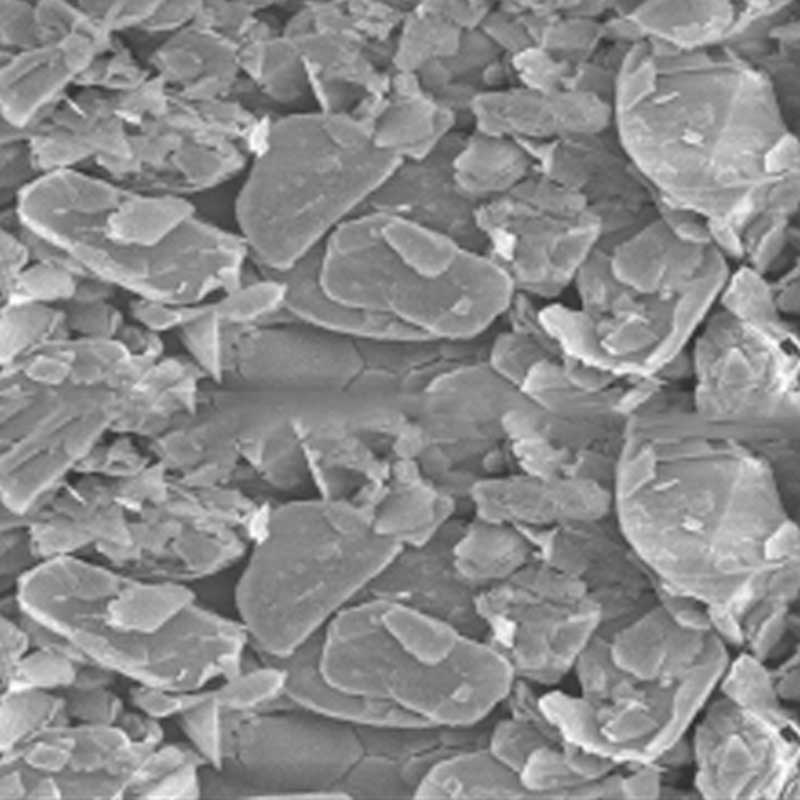
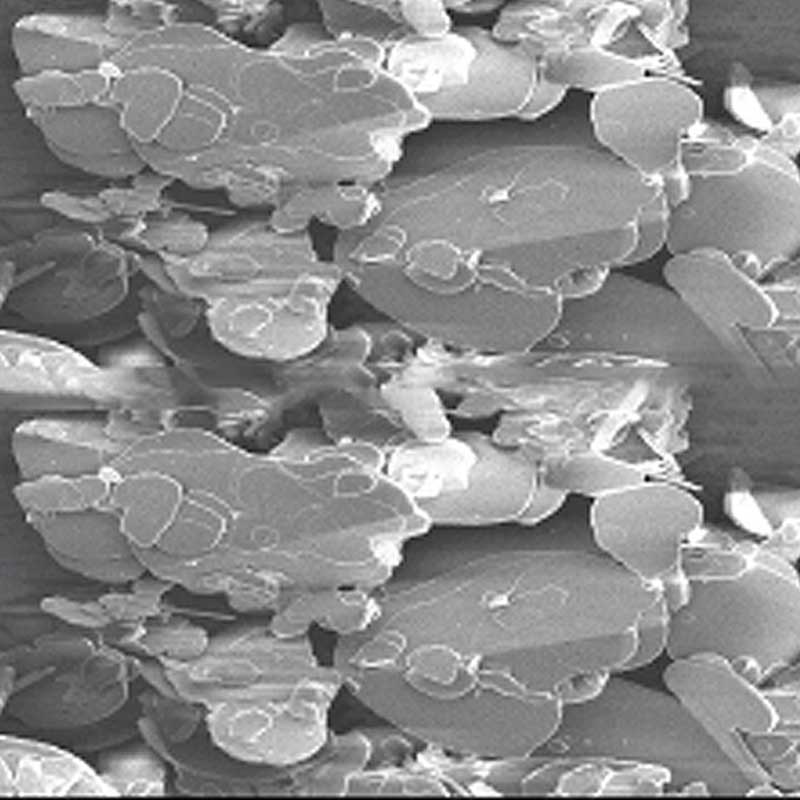
BN - B
BN - B
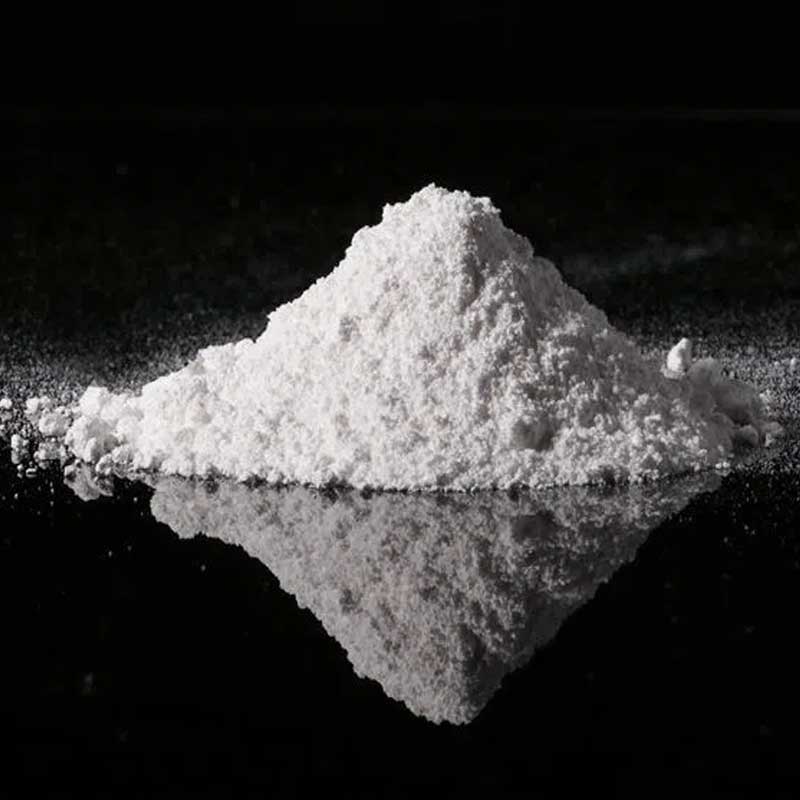
Boron Nitride Powder
Boron nitride powder exhibits exceptional thermal stability, high thermal conductivity, excellent electrical insulation, and resistance to chemical corrosion.
● Special electrolysis and resistance boron nitride insulator under high-temperature conditions.
● High-temperature solid lubricants, extrusion anti-wear additives, ceramic composite additives, refractory materials, and anti-oxidant additives.
● Boron nitride powder is suitable for heat-sealing transistor desiccant and polymer additives, such as plastic resin.
● Boron nitride powder can be pressed into various shapes of the boron products, such as the components for high temperature and high pressure, insulation, and heat dissipation components.
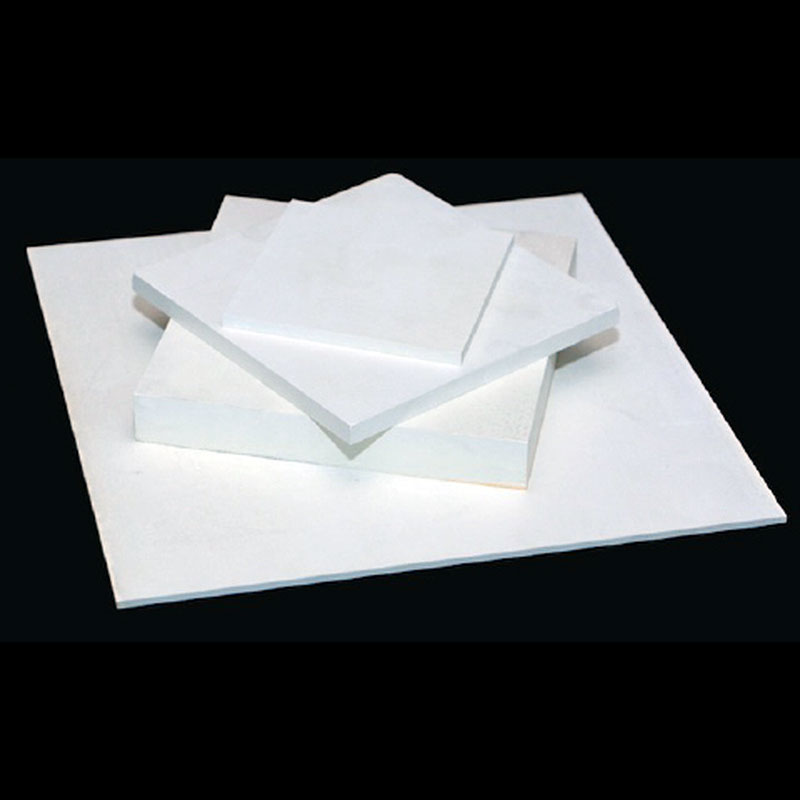
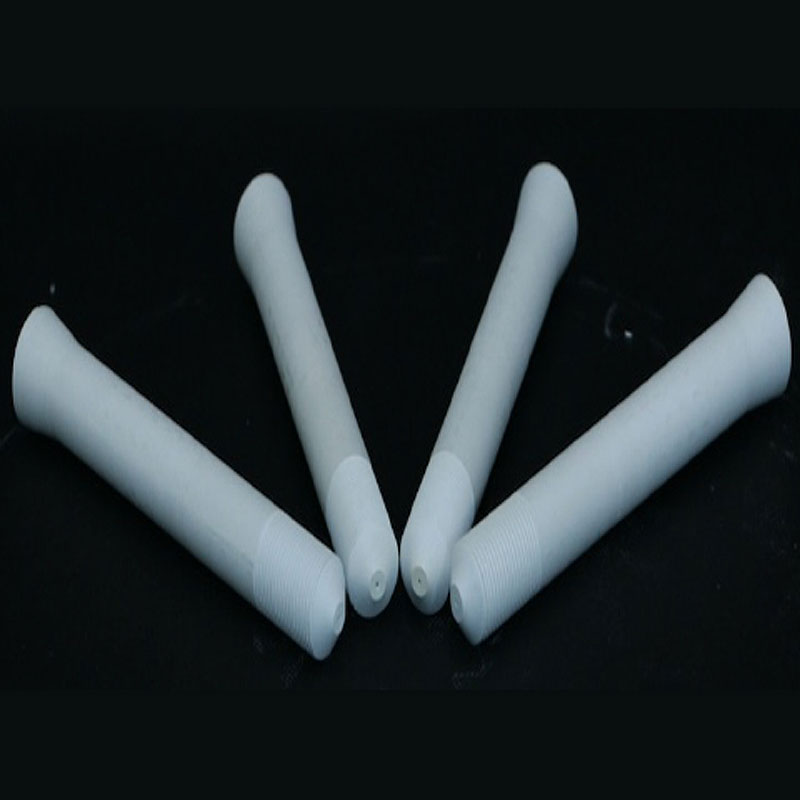
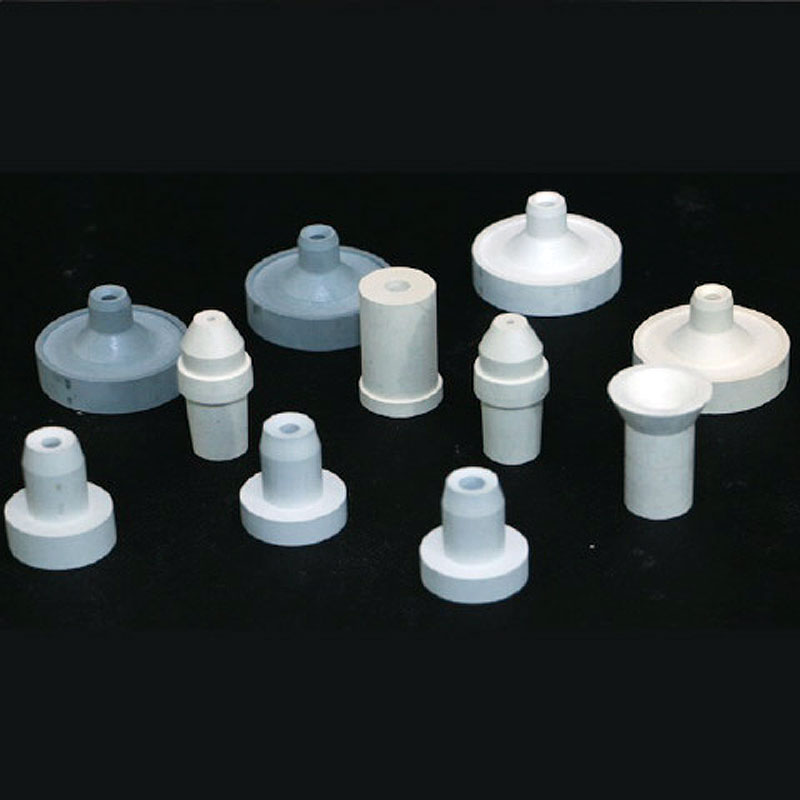
Boron Products of BN-B Boron Nitride Powder Wholesale
Boron nitride powder is used in the electronics industry to manufacture boron products, such as boron nitride insulators, heat sinks, and thermal interface materials. These products facilitate efficient heat dissipation and ensure the reliable operation of electronic components.
Advantages of Boron Nitride Powder
● Remarkable thermal conductivity, to maintain optimal operating temperatures and enhances the performance and reliability of various systems.
● Electrical insulation properties. Providing electrical isolation while allowing for efficient heat transfer.
Applications
● High Thermal Conductivity. Boron nitride powders exhibit excellent thermal conductivity, comparable to other high-performance ceramic materials.
● Electrical Insulation. Boron nitride powder can be produced into a boron nitride insulator. It has a high dielectric strength and low electrical conductivity, making it suitable for applications where electrical insulation is critical, such as in electronics and electrical components.
● Thermal Stability. Boron products possess remarkable thermal stability, allowing them to withstand high temperatures without significant decomposition.
● Chemical Resistance. Boron nitride powder exhibits high chemical resistance and is inert to most chemicals, including acids, bases, and solvents.
| Grade Typical Value | BN-A | BN-B | BN-C | BN-D | BN-E | BN-ES |
| BN(%) | >99.5 | >99.5 | >99.5 | >99.5 | >99.5 | >99.5 |
| B2O3(%) | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 |
| O(%) | <0.3 | <0.3 | <0.3 | <0.3 | <0.3 | <0.3 |
| C(%) | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| Fe(ppm) | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Cr(ppm) | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Ni(ppm) | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Cu(ppm) | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| Mg(ppm) | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 | <10 |
| H2O remaining (%) | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 | <0.2 |
| Particle size (D50) (μm) | 1.7 | 4.5 | 9.5 | 16 | 30 | 38 |
| BET (m2/g) | 30.3 | 11.5 | 9.2 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
Get A Quote